18. Tertiary Landform development
From peneplain to large scale erosion gullies
The shape & geometry of the landforms in the region around Wattle Flat reveal clues about the landform development history. There are also additional markers of former landscapes such as evidence of ancient soil profiles, and river bed deposits.
Basaltic volcanic eruptions in Eastern Australia during the last 50 million years reveal the direction & speed of Australia’s travel over Earth’s surface. Mt Canobolas is one of these.
During the same time span, there has been some localised tectonic warping & faulting causing changes in landform development. Significant sea-level change has been another significant influence on landform development around coastal parts of Australia.
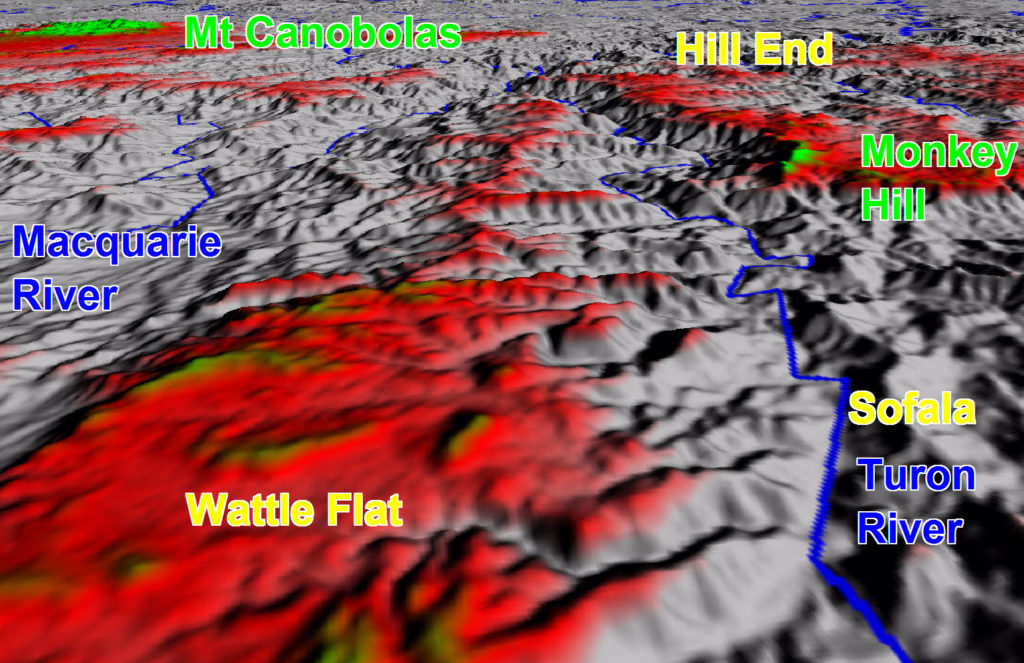
Altitude colour coded digital terrain model looking west from Wattle Flat to Hill End. The red areas reflect likely ancient peneplain landforms

Example of gully erosion for comparison with terrain model

Logarithmic Time Scale – providing world time context relationships. The red box represents this part of story.
Evidence of an ancient Peneplain subsequent incision by energised drainage systems
Mature landscapes developed after extended periods of erosion of elevated lands & infill of lowlands have a characteristic flat horisontal form known as a peneplain. From elevated vantage points in the Wattle Flat area the distant hilltops show a generally flat near horisontal skyline. This is very likely to reflect an ancient peneplain surface. Subsequent juvenile landscape reactivation has resulted in the drainage systems cutting down into this ancient peneplain. The Turon & Macquarie Rivers together with all their tributaries are part of this reactivated landscape. The images about illustrate how this is like large scale gully erosion.
Evidence of ancient soils indicative of a warm wet climate
Across much of eastern NSW, there is widespread evidence of lateritic soil development typically formed by strong leaching under tropical wet climates. The spectacular ironstone bands seen in exposures of Hawkesbury Sandstone all over the Sydney Basin are associated with this lateritic leaching. Some soils around Wattle Flat contain abundant ferruginous pisoliths again suggestive of ancient lateritic soils. This is probably a relic of the early Tertiary land surface conditions
Local Volcanic eruptions eg Mt Canobolas with lava streams following rivers at the time.
The most obvious recently active volcanoe in the Wattle Flat region is Mt Canobolas xxkm to the west. This volcano erupted 11 million years ago. This is a basaltic volcano which produces a very fluid lava capable of flowing very easily across flat surfaces and for great distances along defined river channels. A similar younger volcano( Undara) in North QLD has well defined river channel lava flows upto 100km long. There are several isolated hill tops in the area surrounding Wattle Flat composed of basalt lava overlying river sediment deposits. The closest is Monkey Hill xx km NW of Wattle Flat. It seem possible that the river gravels beneath the Monkey Hill basalt reflect the bed of the Turon River prior to the erosion of the current Turon River valley. Basalt on the top of Mt Panorama & Mt Pleasant in Bathurst may mark the former path of the Macquarie River. Others include Mt Airlie, Mt Wilson group in Blue Mtns
Array of volcanic centers across eastern Australia
During the 2nd half of this Tertiary period from about 30 million years ago to the modern era, there have been numerous volcanic eruptions in eastern Australia. Nearly all of the volcanic systems in this group seem to group into multiple linear sets in which the linear axes have a NNE orientation, and with the older volcanic systems located successively further north along these axes. This configuration strongly suggests that these volcanic eruptions result from deep fixed mantle plumes periodically ascending through the overlying crust as the Australian crustal plate moves in a NNE direction. Mt Canobolas is one of these volcanic systems, that erupted 11 million years ago. The eruption age of these volcanoes range between 30 million years & just a few thousand years ago.