15. Palaeozoic Era (540 - 250 million years ago )
- Formation of the local rocks and gold reefs
–Evolution of complex creatures and plants (in sea and on land)

Logarithmic Time Scale – providing world time context/relationships. The red box represents this part of story.
Explosion of Life: During The Palaeozoic Era, there is a massive explosion & diversification of life forms particularly in warm shallow seas, and subsequently in swampy coastal areas. Flourishing carbon dioxide using marine organisms (cyanobacteria) oxygenate the sea water and atmosphere. This is a catalyst for the evolution of oxygen using creatures: invertebrates, fish, amphibians & reptiles. Plants also evolve dramatically with ferns, cycads & conifers.
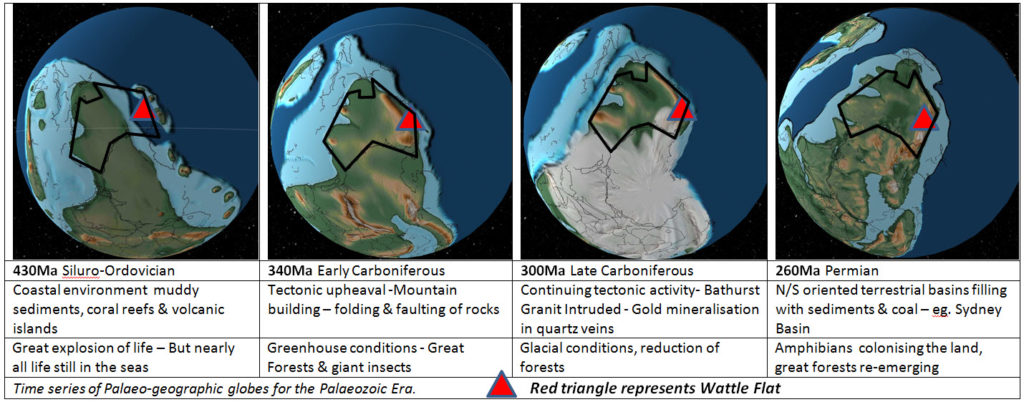
Stage 1: A large proportion of the basement rock in Eastern Australia was deposited during the Palaeozoic Era. The Wattle Flat area is initially (during Ordovician & Silurian time) a broad coastal sedimentary basin with volcanic islands much like the Philippines is today. On a regional scale we are situated along the East coast of the Gondwana supercontinent in which Australia & Antarctica are a continuous landmass.
Stages 2 & 3: Later during the Carboniferous period there are major changes in global tectonics & global climatic conditions. These result from the joining of the Gondwana supercontinent with the northern supercontinent Laurasia to form Pangea. Initially Greenhouse conditions prevail allowing very extensive moss & horsetail forests to flourish. Later, perhaps due to re-routing of global oceanic currents, Ice house conditions were initiated & ice sheets grow to cover much of Australia. In the Wattle Flat area, the former sedimentary basins with localised volcanic piles (Sofala Volcanics), become uplifted, folded & faulted into what would have been a major mountain chain. The massive granite intrusions of Bathurst were emplaced. The gold bearing quartz reef deposits at Wattle Flat are believed to have formed at about this time, along with numerous other gold deposits in Eastern Australia.
Stage 4: In the latest part of the Palaeozoic Era (Permian Period), large N/S oriented troughs develop in which river sediments accumulate and swamp forests flourish. The basal parts of the Sydney Basin beneath the Blue Mountains east of the Wattle Flat area are representative of this.
The End ?: The end of the Palaeozoic Era is defined by an intense global life extinction event (P/T extinction event) which decimated both land & sea ecosystems. It is not clear what caused this, but it is the subject of much research. The few survivors of this catastrophic event evolve & diversify to populate the next era, the Mesozoic.